Scientists have discovered the fossil of an unusual large-bodied sponge-like sea-creature from half a billion years ago, according to Science Daily.
The creature belongs to an obscure and mysterious group of animals known as the chancelloriids, and scientists are unclear about where they fit in the tree of life.
They represent a lineage of spiny tube-shaped animals that arose during the Cambrian evolutionary “explosion” but went extinct soon afterwards. In some ways they resemble sponges, a group of simple filter-feeding animals, but many scientists have dismissed the similarities as superficial.
The new discovery by a team of scientists from the University of Leicester, the University of Oxford and Yunnan University, China, adds new evidence that could help solve the mystery.
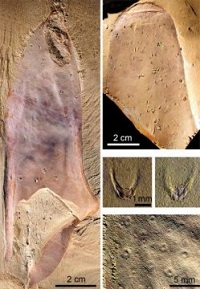
The new species, named Allonnia nuda, was discovered in the Chengjiang deposits of Yunnan Province, China. It was surprisingly large in life (perhaps up to 50 cm or more) but had only a few very tiny spines.
Its unusual “naked” appearance suggests that further specimens may be “hiding in plain sight” in fossil collections, and shows that this group was more diverse than previously thought.
Furthermore, the new species holds clues about the pattern of body growth, with clear links to modern sponges. It is too soon to say the mystery has been solved, but the discovery highlights the central role of sponge-like fossils in the debate over earliest animal evolution.
Dr Tom Harvey, from the University of Leicester’s School of Geography, Geology and the Environment, explained: “Fossil chancelloriids were first described around 100 years ago, but have resisted attempts to place them in the tree of life. We argue that their pattern of body growth supports a link to sponges, reinvigorating an old hypothesis. We’re not suggesting that it’s “case closed” for chancelloriids, but we hope our results will inspire new research into the nature of the earliest animals.”
Dr Peiyun Cong, added: “The Chengjiang deposits continue to reveal surprising new fossils we could hardly have imagined. Together, they provide a crucial snapshot of life in the oceans during the Cambrian explosion.”
N.H.Kh