Dinosaurs’ faces might have been much more sensitive than previously thought, according to a study — helping them with everything from picking flesh from bones to wooing potential mates, according to Science Daily.
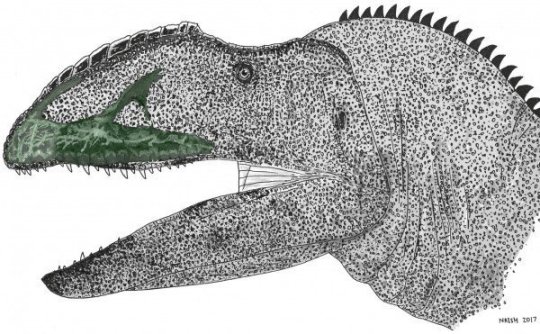
Experts used advanced X-ray and 3D imaging techniques to look inside the fossilised skull of Neovenator salerii — a large carnivorous land-based dinosaur – and found evidence that it possessed an extremely sensitive snout of a kind previously only associated with aquatic feeders.
The blood vessels and nerves that supply the head are poorly documented in dinosaur fossils, but the new study shows that Neovenator may have possessed pressure receptors in the skin of its snout — similar to those which allow crocodiles to forage in murky water.
However, nothing about the 125-million-year-old dinosaur suggests it was an aquatic feeder, so researchers believe it must have developed such a sensitive snout for other purposes.
Chris Barker, who was studying for his Masters degree in Vertebrate Palaeontology when he carried out the research, said: “The 3D picture we built up of the inside of Neovenator‘s skull was more detailed than any of us could have hoped for, revealing the most complete dinosaur neurovascular canal that we know of.
“The canal is highly branched nearest the tip of the snout. This would have housed branches of the large trigeminal nerve — which is responsible for sensation in the face — and associated blood vessels. This suggests that Neovenator had an extremely sensitive snout — a very useful adaptation, as dinosaurs used their heads for most activities.”
As well as being sensitive to touch, Neovenator might also have been able to receive information relating to stimuli such as pressure and temperature, which would have come in useful for many activities — from stroking each other’s faces during courtship rituals to precision feeding.
Images of the wear pattern on the dinosaur’s teeth appear to show that it actively avoided bone while removing flesh from bones.
Chris added: “Some modern-day species, such as crocodilians and megapode birds, use their snout to measure nest temperature, and in the case of crocodiles even pick up their young with extreme care, despite their huge mouths. Neovenator might well have done the same.
“Having such a sensitive snout could have had a social use too. Many birds — which are the descendants of dinosaurs — use their beaks in social display, and there is plenty of evidence that carnivorous dinosaurs engaged in face-biting among themselves, perhaps targeting the sensitivity of the face to make a point.”
Elis Newham, who was also involved in the study, commented: “This finding comes at an exciting time in palaeontology, where we are using state-of-the-art technology to shed new light on the physiologies of extinct animals.
“Our results add a new level of detail to our understanding of the way large predatory dinosaurs interacted with the world around them. The range of exciting possibilities for such facial sensitivity show just how far we have come in our re-assessment of dinosaurs from lumbering beasts to complex, highly adapted organisms.”
N.H.Kh