Research into lethal wounds found on a human skull may indicate one of the first cases of murder in human history — some 430,000 years ago — and offers evidence of the earliest funerary practices in the archaeological record.
The study, conducted by an international team was carried out at the archeological site of the Sima de los Huesos in northern Spain. The site is located deep within an underground cave system and contains the skeletal remains of at least 28 individuals that date to around 430,000 years ago, during the Middle Pleistocene time period. The only access to the site is through a 13-meter deep vertical shaft.
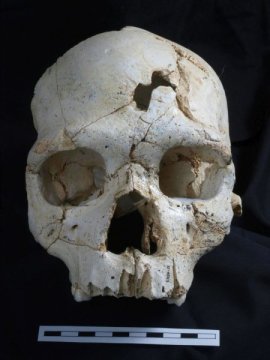
A nearly complete skull, Cranium 17, from the Sima de los Huesos is composed of 52 cranial fragments recovered during excavations at the site over the last 20 years. This skull shows two penetrating lesions on the frontal bone, above the left eye. “Evidence for interpersonal violence in the human fossil record is relatively scarce, and this would appear to represent the coldest cold case on record,” said Quam.
Relying on modern forensic techniques, such as contour and trajectory analysis of the traumas, the authors of the study showed that both fractures were likely produced by two separate impacts by the same object, with slightly different trajectories around the time of the individual’s death. According to the authors, the injuries are unlikely to be the result of an accidental fall down the vertical shaft. Rather, the type of fracture, their location and that they appear to have been produced by two blows with the same object lead the authors to interpret them as the result of an act of lethal interpersonal aggression — or what may constitute the earliest case of murder in human history.
Furthermore, if this individual was already dead, other humans likely carried them to the top of the vertical shaft. The authors suggest that humans were likely responsible for the accumulation of bodies in the Sima de los Huesos, which supports the idea that this site represents early evidence of funerary behavior.
“This is really good evidence for an intentional role for humans in the accumulation of bodies at the bottom of this pit and suggests the hominins from this time period were already engaging in complex cognitive behaviors,” said Quam.
Source: Science daily
N.H.Khider