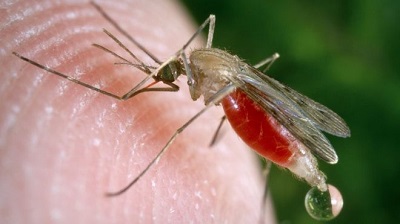
A fungus – genetically enhanced to produce spider toxin – can rapidly kill huge numbers of the mosquitoes that spread malaria, a study suggests.
Trials, which took place in Burkina Faso, showed mosquito populations collapsed by 99% within 45 days, according to BBC.
The researchers say their aim is not to make the insects extinct but to help stop the spread of malaria.
The disease, which is spread when female mosquitoes drink blood, kills more than 400,000 people per year.
Worldwide, there are about 219 million cases of malaria each year.
Would it be wrong to eradicate mosquitoes?
Working the night shift on Malaria’s frontline in Sierra Leone
Africa pilots world’s first malaria vaccine in major trial
Conducting the study, researchers at the University of Maryland in the US – and the IRSS research institute in Burkina Faso – first identified a fungus called Metarhizium pingshaense, which naturally infects the Anopheles mosquitoes that spread malaria.
The next stage was to enhance the fungus. “They’re very malleable, you can genetically engineer them very easily,” Prof Raymond St Leger, from the University of Maryland, told BBC News.
They turned to a toxin found in the venom of a species of funnel-web spider in Australia.
The genetic instructions for making the toxin were added to the fungus’s own genetic code so it would start making the toxin once it was inside a mosquito.
“A spider uses its fangs to pierce the skin of insects and inject toxins, we replaced the fangs of spider with Metarhizium,” Prof St Leger explained.
Laboratory tests showed the genetically modified fungus could kill quicker, and that it took fewer fungal spores to do the job. The next step was to test the fungus in as close to real-world conditions as possible.
A 6,500-sq-ft fake village – complete with plants, huts, water sources and food for the mosquitoes – was set up in Burkina Faso. It was surrounded by a double layer of mosquito netting to prevent anything escaping.
The fungal spores were mixed with sesame oil and wiped on to black cotton sheets. The mosquitoes had to land on the sheets to be exposed to the deadly fungus. The researchers started the experiments with 1,500 mosquitoes.
The results, showed numbers soared when the insects were left alone. But when the spider-toxin fungus was used, there were just 13 mosquitoes left after 45 days.
New tools are needed to tackle malaria as mosquitoes are becoming resistant to insecticides. The World Health Organization has warned that cases are now increasing in the 10 worst affected countries in Africa.
H.Z