Scientists have discovered why the ‘broken world’ following the worst extinction of all time lasted so long — it was simply too hot to survive.
Scientists have discovered why the ‘broken world’ following the worst extinction of all time lasted so long — it was simply too hot to survive.
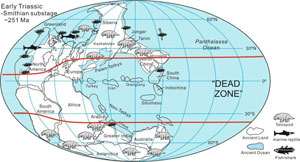
The end-Permian mass extinction, which occurred around 250 million years ago in the pre-dinosaur era, wiped out nearly all the world’s species. Typically, a mass extinction is followed by a ‘dead zone’ during which new species are not seen for tens of thousands of years. In this case, the dead zone, during the Early Triassic period which followed, lasted for a perplexingly long period: five million years.
A study jointly led by the University of Leeds and China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), in collaboration with the University of Erlangen-Nurnburg (Germany), shows the cause of this lengthy devastation was a temperature rise to lethal levels in the tropics: around 50-60°C on land, and 40°C at the sea-surface.
Lead author Yadong Sun, who is based in Leeds while completing a joint PhD in geology, says: “Global warming has long been linked to the end-Permian mass extinction, but this study is the first to show extreme temperatures kept life from re-starting in Equatorial latitudes for millions of years.”
It is also the first study to show water temperatures close to the ocean’s surface can reach 40°C — a near-lethal value at which marine life dies and photosynthesis stops. Until now, climate modellers have assumed sea-surface temperatures cannot surpass 30°C. The findings may help us understand future climate change patterns.
The dead zone would have been a strange world — very wet in the tropics but with almost nothing growing. No forests grew, only shrubs and ferns. No fish or marine reptiles were to be found in the tropics, only shellfish, and virtually no land animals existed because their high metabolic rate made it impossible to deal with the extreme temperatures. Only the polar regions provided a refuge from the baking heat.
Before the end-Permian mass extinction, Earth had teemed with plants and animals including primitive reptiles and amphibians, and a wide variety of sea creatures including coral and sea lillies.
.
ScienceDaily