Two monkeys grooming each other about 20-30 million years ago may have helped produce a remarkable new find — the first fossilized red blood cells from a mammal, preserved so perfectly in amber that they appear to have been prepared for display in a laboratory. According to Science daily
The discovery, also describes the only known fossils of a type of parasite that still exists today, Babesia microti, which infects the blood cells of humans and other animals.
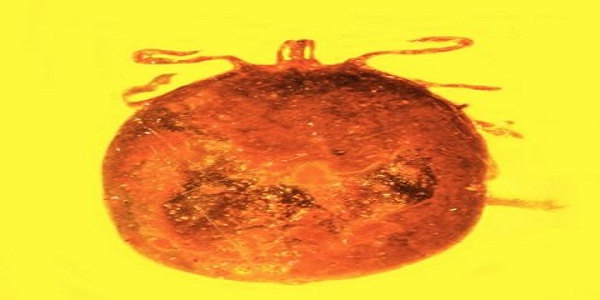
Two small holes in the back of a blood-engorged tick, which allowed blood to ooze out just as the tick became stuck in tree sap that later fossilized into amber, provide a brief glimpse of life in a tropical jungle millions of years ago.
“These two tiny holes indicate that something picked a tick off the mammal it was feeding on, puncturing it in the process and dropping it immediately into tree sap,” said George Poinar, Jr., professor emeritus, author of the study and animal life forms found preserved in amber.
“This would be consistent with the grooming behavior of monkeys that we know lived at that time in this region. The fossilized blood cells, infected with these parasites, are simply amazing in their detail. This discovery provides the only known fossils of Babesia-type pathogens.”
The fossil parasites add to the history of the Order Piroplasmida, of which the Babesiidae is one family. In humans, the parasite B. microti can cause babesiosis, a disease with symptoms that resemble malaria and can be fatal. A related parasite in cattle can cause cattle fever, which has been a historic problem in the plains, and just this spring is causing another outbreak that has led to quarantines on more than 500,000 acres of land.
“The life forms we find in amber can reveal so much about the history and evolution of diseases we still struggle with today,” Poinar said. “This parasite, for instance, was clearly around millions of years before humans, and appears to have evolved alongside primates, among other hosts.”
Part of what makes these fossils unique, Poinar said, is the clarity by which the parasites and blood cells are preserved, almost as if they had been stained and otherwise treated in a laboratory. The parasites were different enough in texture and density to stand out clearly within the red blood cells during the natural embalming process for which amber is famous.
N.H.Kh